License Management
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 11.0.
Overview
If you are using GitLab CI/CD, you can search your project dependencies for their licenses
using License Management, either by
including the CI job in your existing .gitlab-ci.yml file or
by implicitly using Auto License Management
that is provided by Auto DevOps.
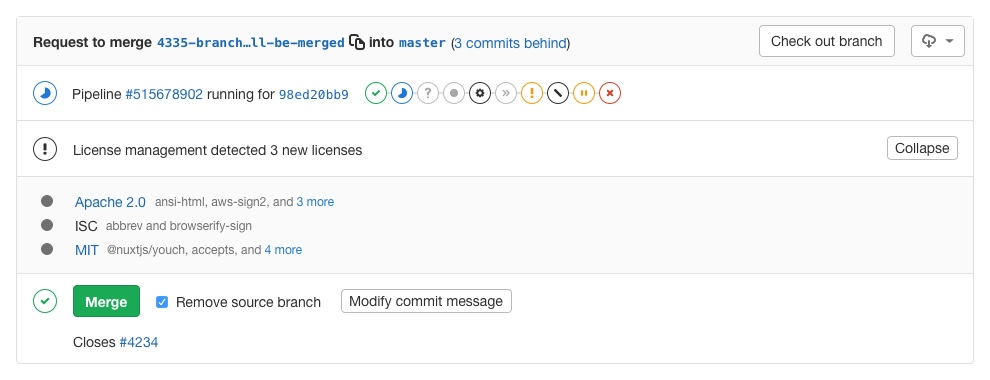
Going a step further, GitLab can show the licenses list right in the merge request widget area.
Use cases
It helps you find licenses that you don't want to use in your project and see which dependencies use them. For example, your application is using an external (open source) library whose license is incompatible with yours.
Supported languages and package managers
The following languages and package managers are supported.
| Language | Package managers |
|---|---|
| JavaScript | Bower, npm |
| Go | Godep, go get |
| Java | Gradle, Maven |
| .NET | Nuget |
| Python | pip |
| Ruby | gem |
How it works
First of all, you need to define a job named license_management in your
.gitlab-ci.yml file. Check how the license_management job should look like.
In order for the report to show in the merge request, there are two prerequisites:
- the specified job must be named
license_management - the resulting report must be named
gl-license-management-report.jsonand uploaded as an artifact
Note: If the license management report doesn't have anything to compare to, no information will be displayed in the merge request area. That is the case when you add the
license_managementjob in your.gitlab-ci.ymlfor the very first time. Consecutive merge requests will have something to compare to and the license management report will be shown properly.
The license_management job will search the application dependencies for licenses,
the resulting JSON file will be uploaded as an artifact, and
GitLab will then check this file and show the information inside the merge
request.